Key Points:
- Supplementing 3TC to both naturally aged mice and mice modeling neurodegeneration improves memory deficits.
- Mice treated with 3TC exhibit lower levels of inflammatory markers in the brain.
DNA, the blueprint of life, is a mysterious molecular tapestry that is the foundation of our existence, dictating everything from our traits to how we age. This twisting ladder of genetic information holds the code that is key to unlocking the secrets of preserving health and vitality. Within this code, scientists have identified transposable elements (TEs) – short mobile DNA sequences capable of shifting their position within the entire DNA sequence – as potential targets to mitigate age-related diseases, particularly cognitive dysfunction.
In a new study published in Aging Cell, researchers from Colorado State University explored the cognitive protective effects of 3TC, a known inhibitor of TE dysregulation. Wahl and colleagues showed that supplementing 3TC in 19-month-old naturally aged mice and 2-month-old genetically modified mice modeling neurodegeneration was sufficient to boost cognitive function. What’s more, the investigators found that 3TC treatment reduced multiple markers of inflammation in the brain.
The Role of Transposable Elements in Aging
TEs are extremely multifaceted in nature and vary between organisms. Because of this, scientists have yet to pinpoint the underlying role of TEs in aging. For a long time, many scientists referred to these short DNA sequences as “junk DNA.” Although, this is far from the truth. TEs are comprised of multiple DNA elements (promoters, enhancers, transcription factor binding sites) that play a major role in dictating which genes are turned on or off, regulating various cellular pathways. So, when TEs jump from one area of DNA to another, which creates a new TE sequence, the gene-regulating factors within TEs have the potential to rearrange DNA and impact gene activity. However, this can lead to unwarranted genetic mutations that compromise the genome, leading to the development of age-related diseases. Thus, aging scientists have searched for therapeutics capable of inhibiting TEs.
3TC Mitigates Age-Related Cognitive Dysfunction
TE dysregulation naturally occurs with age and ultimately leads to increases in TEs, which has been shown to trigger systemic inflammation – a hallmark of aging and cognitive decline. Accordingly, researchers have honed in on TE inhibitors, like 3TC, to thwart TE accumulation, as they have been found to deter the formation of new TEs across DNA. Before examining the effects of 3TC on cognition, the investigators confirmed that the old mice used in the study exhibited age-related increases in TEs, allowing them to elucidate the relationship between elevated TEs and cognitive dysfunction.
Wahl and colleagues employed the Barnes Maze test for four days to assess spatial memory, a cognitive function that takes a major hit with age. Here, mice were placed on a circular white table with 20 equally spaced holes around the perimeter and given one minute to locate the escape hole. Compared to young mice, untreated aged mice took significantly longer to find the escape hole. However, by the fourth day of testing, those treated with 3TC completed the challenge much quicker than untreated aged mice, displaying similar times to those achieved in young mice. The investigators repeated testing but removed the escape hole to see whether the mice remembered its location. As expected, treated mice spent more time exploring the quadrant where the escape hole was located than untreated mice, indicating retained spacial memory improvements.
The Colorado researchers then conducted the novel object recognition test to evaluate changes in recognition memory, a common feature of Alzheimer’s. This test evaluated the spontaneous tendency of mice to allocate more time exploring a novel object than a familiar one, which signifies superior memory. The results showed that mice treated with 3TC spent significantly more time exploring the novel object than untreated mice, demonstrating enhanced recognition memory.
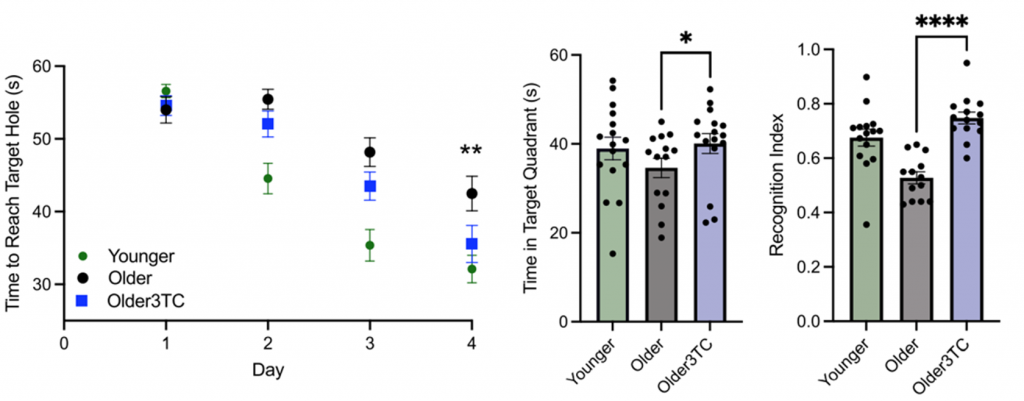
To further explore the effects of 3TC on age-related cognitive decline, the investigators conducted similar cognitive tests in genetically modified (transgenic) mice carrying increased levels of Tau – an Alzheimer’s-related protein linked to increases in TE. Notably, 3TC-treated transgenic mice outperformed their untreated counterparts in all cognitive tests, further demonstrating that 3TC attenuates memory decline. Overall, the findings suggest that 3TC holds potent cognitive protective properties.
3TC Reduces Brain Inflammation
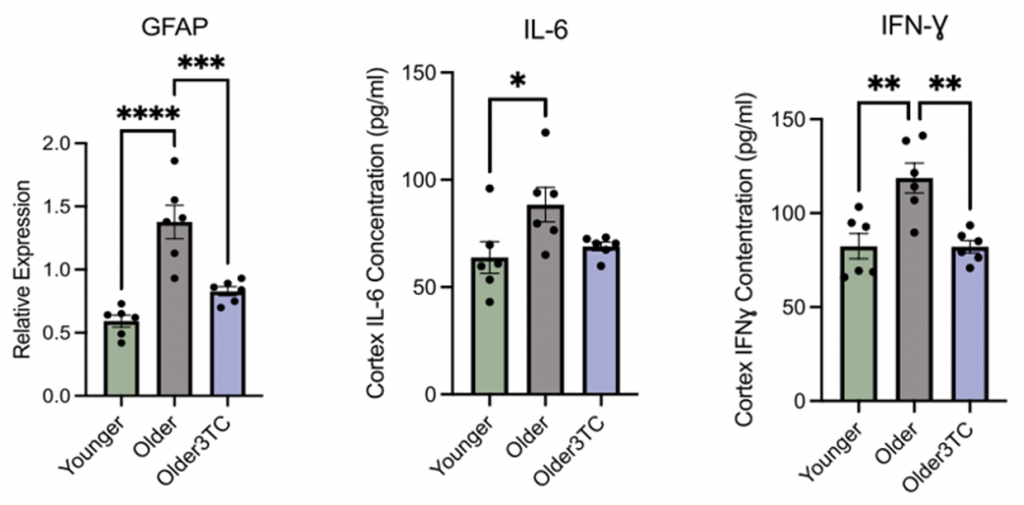
Given that inflammation drives neurodegeneration, Wahl and colleagues looked at the levels of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), which has strong ties to elevated inflammation and cognitive dysfunction. While untreated aged mice exhibited higher levels of GFAP than young mice, mice treated with 3TC displayed GFAP levels similar to young mice, highlighting that 3TC attenuated age-related increases in brain inflammation.
The investigators also examined the levels of pro-inflammatory molecules (IL-6, IFNɣ) central to the immune response during TE dysregulation. Accordingly, both markers significantly increased in untreated aged mice; however, IL-6 and IFNɣ levels dropped following treatment with 3TC, although only IFNɣ reached statistical significance. These findings reveal that the cognitive boosting effects of 3TC likely stem from its role in regulating markers of inflammation and immune responses.
Transposable Elements: New Targets of Aging
Although preclinical studies have established the link between TEs and aging, whether this translates to humans remains unclear. However, in this study, Wahl and colleagues conducted additional genetic analysis on humans to shed light on this matter. The data revealed that human brains also exhibit age-related increases in TEs, some of which influence neurodegeneration and cellular senescence – a state of cell cycle arrest that promotes aging. Notably, some of the identified TEs in the healthy-aged humans overlapped with those found in brains with tau pathology, further confirming that TEs may promote brain aging and cognitive decline.
Collectively, the study’s findings suggest that inhibitors of TE dysregulation, like 3TC, should undergo further research to assess human translatability, as it can potentially mitigate multiple features of aging. Currently, 3TC is prescribed as an anti-viral drug to treat hepatitis B and HIV. Although uncommon, 3TC can potentially cause mitochondrial toxicity, which can increase susceptibility to liver failure and muscle weakness.