Key Points:
- Supplementing mice with GlyNAC increases lifespan by 24%.
- GlyNAC replenishes the natural antioxidant glutathione (GSH) and attenuates multiple aging hallmarks: mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and DNA damage.
The harmonious balance between oxidants and antioxidants is vital to sustaining cellular functions critical for longevity. One way our bodies achieve this equilibrium is through the abundant antioxidant glutathione (GSH). GSH depletes upon aging and contributes to the onset of multiple aging hallmarks, namely mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and DNA damage. Fortunately, scientists have pinpointed a potent antioxidant cocktail (GlyNAC) that restores GSH levels.
In a new study published in Nutrients, researchers from Baylor College of Medicine explore whether GlyNAC leads to increased longevity. The investigators found that supplementing old mice with GlyNAC increases their lifespan by 24%. Additionally, GlyNAC reduces oxidative stress and ameliorates aging hallmarks linked to GSH depletion: mitochondrial dysfunction and DNA damage.
GlyNAC Increases Lifespan and Boosts Mitochondrial Function
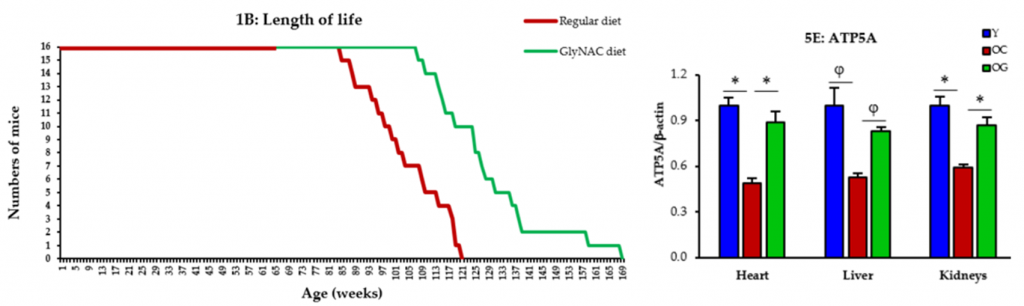
To examine the clinical effects of GlyNAC supplementation on longevity, Kumar and colleagues placed 65-week-old mice on a controlled diet containing 1.6 mg/g of N-acetylcysteine (NAC) and 1.6 mg/g of glycine (Gly) for the remainder of their natural lives. The findings showed that GlyNac-supplemented mice live 24% longer than mice on a regular diet, demonstrating that GlyNAC significantly boosts longevity.
Increased oxidative stress driven by reactive oxygen species (ROS) upon aging inevitably compromises our cellular powerhouses (mitochondria), and when this happens, our cell’s energy currency (ATP) falls. Without ATP, life would cease to exist. Accordingly, the Baylor researchers found that GlyNAC mitigates oxidative stress and restores ATP to youthful levels in the heart, liver, and kidneys. Taken together, these initial findings suggest that GlyNAC increases lifespan by regulating oxidative stress and boosting mitochondrial function.
GlyNAC Protects DNA
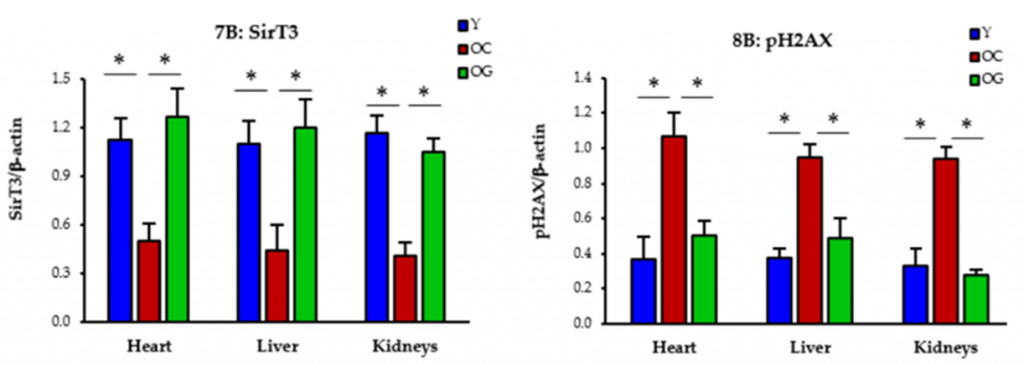
Damage to our genetic blueprints (DNA) underlies nearly all age-related diseases. Thus, DNA repair mechanisms are vital to longevity. Upon DNA damage, our cells harness the power of guardian proteins called sirtuins. These essential proteins help recruit key proteins like NAD+ that trigger the cellular machinery needed to repair DNA.
Moreover, Kumar and colleagues show that GlyNAC-supplemented mice exhibit higher sirtuin activity in the heart, liver, and kidneys, with Sirt3 (a specific type of sirtuin) protein levels being similar to those of young mice. Notably, GlyNAC-supplemented mice also exhibit much lower DNA damage than untreated mice, highlighting that GlyNAC potentially promotes healthy aging by protecting DNA through elevated sirtuin activity.
Does GlyNAC Work in Humans?
Human studies with GlyNAC have sparked some excitement in the scientific community. One study revealed that older adults who took GlyNAC had improved cognition and increased physical function, highlighting GlyNAC’s potential role in mitigating critical functions that decline with age. What makes these findings even more exciting is that GlyNAC was well tolerated with no apparent adverse effects, demonstrating GlyNAC’s safety for consumption. Notably, GlyNAC supplementation has also been shown to boost mitophagy – the clearance of defective/dead mitochondria – which also has strong ties to increased longevity in multiple animal studies. Although GlyNAC appears to exert strong protective effects against aging, further research is needed to fully comprehend its nature.