Key Points:
- Old rats injected with stem cell EVs from newborn rats exhibit 60% higher survival rates.
- Young EVs improve the treadmill exercise capacity of old rats.
- Old rat heart function is significantly improved by treatment with young EVs.
Today it seems possible to treat multiple age-related diseases, including cardiovascular disease and diabetes with a single treatment. Now researchers from Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles may have discovered such a treatment.
As reported in Scientific Reports, Shamagian and colleagues show that stem cell EVs prolong the lifespan of old rats. They also show that EVs improve the exercise capacity and heart function of old rats while reducing damage to the heart, skeletal muscle, lungs, and kidneys. These findings suggest that EVs can potentially target multiple age-related diseases.
Stem Cell Extracellular Vesicles Counter Aging
Scientists have suspected that EVs — which are secreted into the blood and affect the entire body — contribute to the rejuvenating effects of young blood. For this reason, Samagian and colleagues isolated heart stem cell EVs from newborn rats. The EVs were then injected into old (22-month-old) rats to determine their rejuvenation effects.
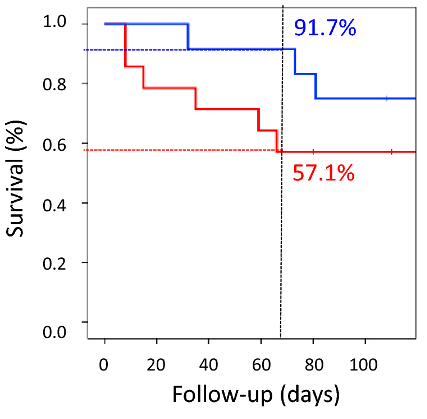
After 16 weeks, 91.7% of the EV-treated old rats survived, whereas only 57.1% of the untreated old rats survived. On average, EV treatment delayed death by 54 days, which is equivalent to about 3.2 human years. The most frequent cause of death was leukemia, accounting for 50% of deaths in untreated old rats and 28% in EV-treated old rats.
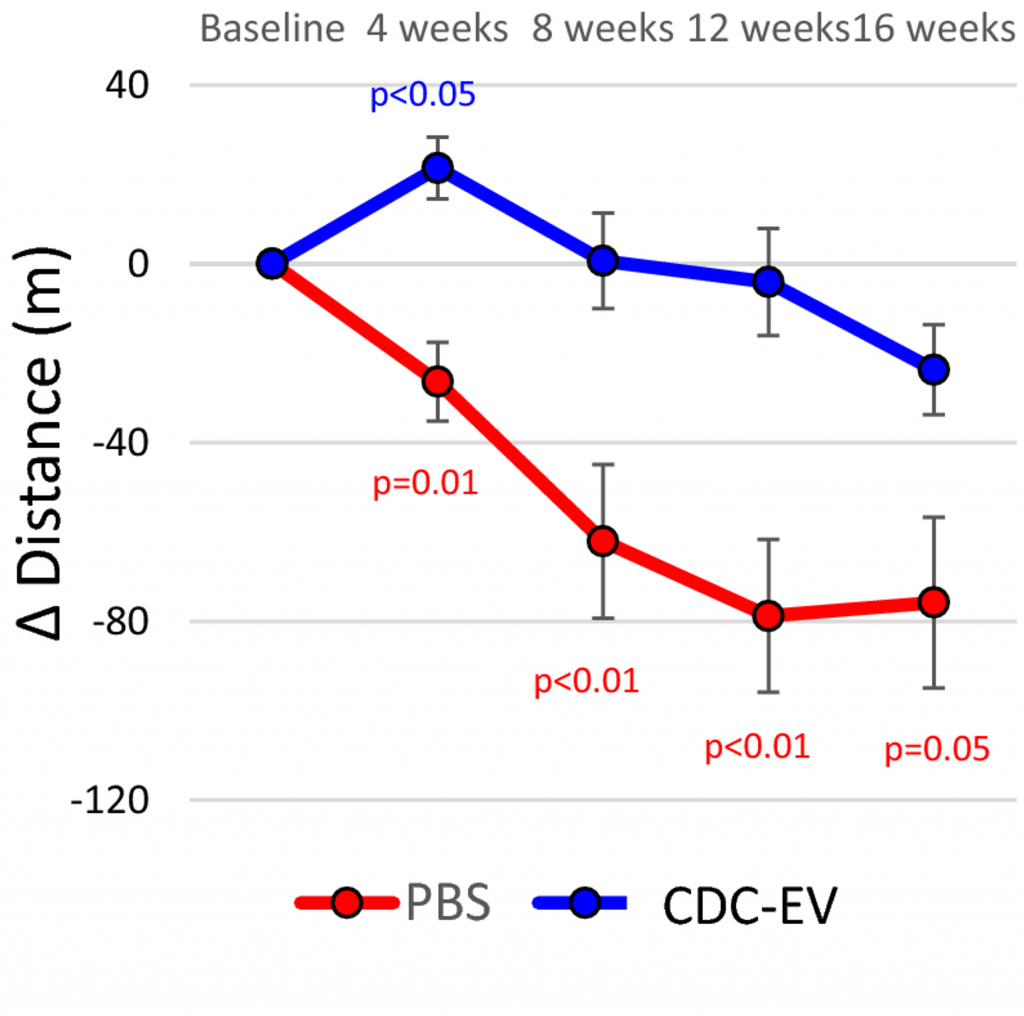
To determine the exercise capacity of the old rats, Shamagian and colleagues challenged the rats to treadmill running every 4 weeks. To exhaust the rats, the speed of the treadmill was increased every 3 minutes, and the distance the rats ran before exhaustion was measured. After the first 4 weeks, the EV-treated old rats ran a 16% longer distance than untreated rats. This increase in distance persisted over 16 weeks, suggesting that EVs improve exercise capacity.
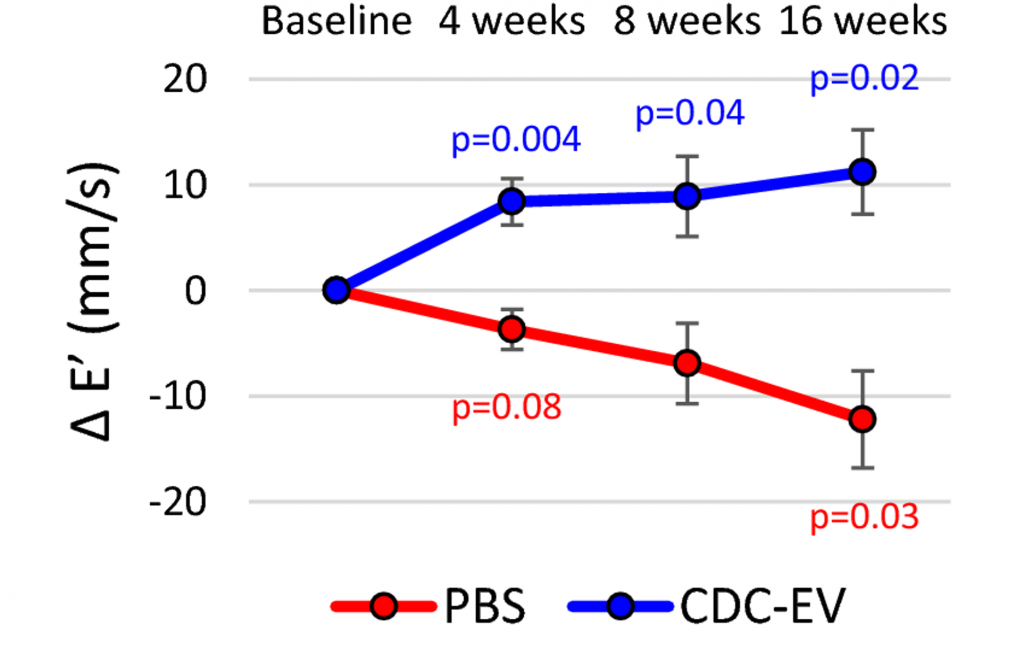
To assess heart function, Shamagian and colleagues measured the velocity of blood flow between chambers of the heart. They found that old rats had reduced blood flow velocity, indicating stiffness and a lack of heart muscle relaxation. However, EV treatment increased blood flow velocity, suggesting that EVs can restore heart function in old rats.
Overall, the findings of Shamagian and colleagues suggest that heart stem cell EVs from newborn rats rejuvenate the hearts of old rats, improving their exercise capacity and prolonging their lifespan. Furthermore, the researchers showed that EVs reduce damage to multiple organs (i.e. heart, lung, kidney, and skeletal muscle), suggesting that young EVs possess rejuvenation effects similar to transferring blood from younger to older organisms (heterochronic parabiosis).
Anti-Aging EVs
EVs secreted by stem cells contain a host of molecules capable of thwarting the processes that underlie aging. These molecules include growth factors, which were previously used to treat arthritis in rats. EVs also contain microRNAs — short strands of RNA that control whether genes are translated to proteins — which have been shown to remove pesky senescent cells. Furthermore, stem cell EVs have been shown to increase grip strength, and even promote hair regrowth in mice. Therefore, we may see young stem cell EVs and their contents being used as treatments for disease in the near future.