Key Points
- After reducing liver blood flow and then restoring it (ischemia-reperfusion) to induce injury, the nutraceutical cocktail prevents liver cell (hepatocyte) programmed cell death (apoptosis).
- The nutraceuticals prevent apoptosis by reducing the production of caspase 3.
- Following the injury, liver tissue treated with the nutraceutical solution showed lower tissue inflammation, premature cell death, and abnormal fat buildup.
Nutraceuticals like nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+)-boosting niacin have been shown to alleviate and prevent aging-associated health conditions like metabolic disorders and cardiovascular disease. Recently, researchers have begun focusing on their synergistic benefits when consumed in combination.
Published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences, Galvao and colleagues from the University of Sao Paulo School of Medicine in Brazil show that supplementing rats with a solution of nutraceuticals including resveratrol, quercetin, omega-3 fatty acid, selenium, ginger, avocado, leucine, and niacin protects the liver against ischemia-reperfusion damage. The nutraceutical cocktail works against liver injury by preventing hepatocyte apoptosis. The means by which the nutraceutical solution alleviates hepatocyte apoptosis includes reducing levels of the pro-apoptotic protein caspase 3. These findings suggest that the nutraceutical combination can prevent excessive and potentially deadly liver injury during ischemia-reperfusion from liver transplants. The study also highlights the possibility that nutraceuticals combined can more generally prevent organ damage from cardiovascular issues with age.
The Solution of Nutraceuticals Protects the Liver Against Altered Blood Flow-Induced Injury
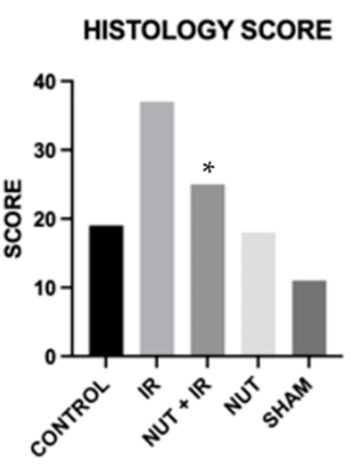
To find out whether the combination of nutraceuticals prevents liver injury following ischemia-reperfusion, Galvao and colleagues examined liver tissue under a microscope. Liver tissue that underwent ischemia-reperfusion displayed much more damage, premature cell death, and aberrant fat deposits culminating in elevated histology scores compared to livers that didn’t go through ischemia-reperfusion. The additional treatment of rats with the nutraceutical cocktail prior to the ischemia-reperfusion significantly lowered the histology score, indicating that the nutraceuticals protect against ischemia-reperfusion-induced liver injury.
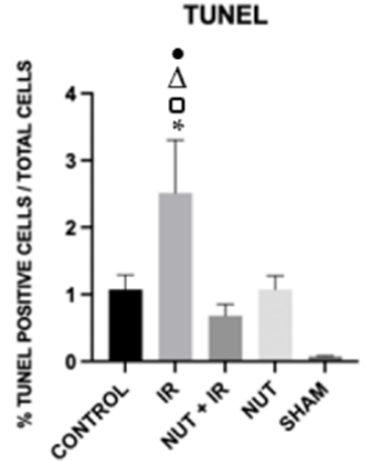
Galvao and colleagues took a closer look at liver cells following ischemia-reperfusion to find out whether the procedure induced apoptosis. Interestingly, undergoing ischemia-reperfusion more than doubled the number of apoptotic hepatocytes, but treatment with the nutraceutical solution before the procedure prevented apoptosis. These data show that the nutraceutical solution preserves the liver against ischemia-reperfusion by blocking apoptosis of hepatocytes.
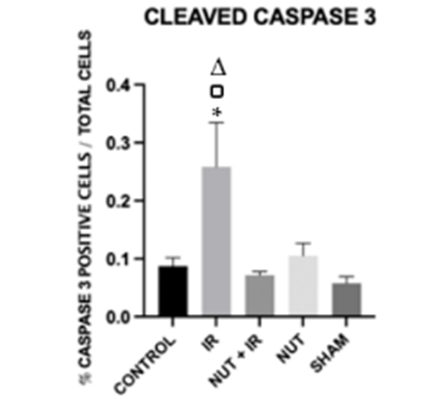
To reach a better understanding of how the nutraceutical cocktail prevents apoptosis to prevent liver injury, Galvao and colleagues examined its effects on the pro-apoptotic protein caspase 3. They found that while ischemia-reperfusion drastically increased the number of hepatocytes exhibiting caspase 3, the nutraceutical solution treatment significantly lowered caspase 3 levels after the ischemia-reperfusion procedure. These results signify that the nutraceutical combination protects the liver against altered blood flow-related injury by preventing caspase 3-induced apoptosis. This also means that other drugs like IDN-6556, which specifically target and inhibit caspase proteins, could also aid in protecting livers from injury.
“We proposed a nutraceutical solution that was able to decrease apoptosis and histologic injury caused by liver [ischemia-reperfusion injury],” said Galvao and colleagues. “Besides transplantation, hepatocyte apoptosis also occurs in chronic liver diseases that affect 1.5 billion persons globally. All these patients can be helped by controlling apoptosis.”
The Possibility that the Nutraceutical Combination Protects Multiple Organs
The study showed that the nutraceutical combination works synergistically to lower the number of hepatocytes exhibiting the pro-apoptotic protein caspase 3, to prevent apoptosis, and protect the liver against injury in the face of an ischemia-reperfusion procedure. The question remains whether these findings are limited to the liver or whether the nutraceutical combination used in the study prevents apoptosis in other organs, thereby preventing damage. If the nutraceutical solution used in the study protects other organs, these nutraceuticals may help to prevent age-related conditions like cardiovascular problems, metabolic complications, and neurological diseases.