Key Points:
- NR replenishes NAD+ in human cells only in the presence of Immucillin H (ImmH).
- Combining NR with ImmH increases the survival rate of NAD+-depleted human cells.
- The NAD+ boosting effect of NR is enhanced by ImmH in the kidneys of mice.
Our cells demand adequate NAD+ levels to fuel enzymes that modulate cell survival. As we age, our cells accumulate damage, namely to DNA, increasing the need for survival enzymes and raising the demand for NAD+. However, when these demands are unmet, cells die, organs degenerate, and disease ensues. This is why replenishing NAD+ has become an attractive anti-aging strategy. Yet, the best way to increase NAD+ levels for specific organs/diseases remains unclear.
As published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry, researchers from the Russian Academy of Sciences have determined how to increase the effectiveness of the NAD+ precursor NR. In human cells challenged with disease-like NAD+ depletion, NR increases NAD+ levels only in the presence of ImmH. Additionally, combining NR with ImmH reduces cell death caused by NAD+ depletion. Furthermore, the NAD+ boosting effect of NR is enhanced by ImmH in the kidneys of mice. These findings suggest that NR combined with ImmH may be effective in combating kidney disease and age-related NAD+ decline.
NR Restores NAD+ Only When Combined with Immucillin H
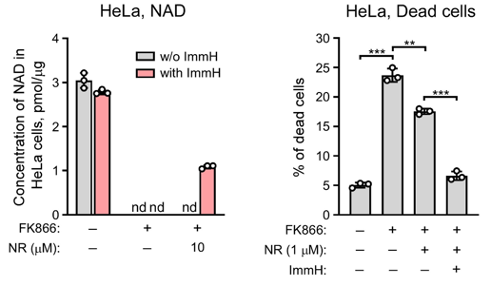
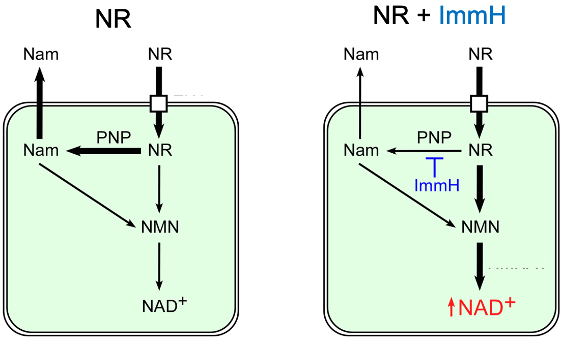
Once NR gets into cells, it can either be converted to NAD+ or broken down by a specific enzyme (purine nucleoside phosphorylase). In multiple human cell types, Kropotov and colleagues confirmed that the breakdown of NR can be prevented by inhibiting this enzyme with ImmH, a molecule approved in Japan as a treatment for T-cell lymphoma under the name Mundesine.
In age-related diseases like heart disease, NAD+ is depleted due, in part, to the reduced activity of an enzyme called NAMPT. Kropotov and colleagues inhibited NAMPT in human cells to cause a rapid drop in NAD+ levels and cell death. Adding NR to these NAD+-depleted cells did not recover NAD+ levels. However, combining NR with ImmH recovered NAD+ up to 50% and increased cell survival. These results demonstrate that ImmH improves the ability of cells to synthesize NAD+ from NR and rescue cells from death in the face of NAD+ depletion.
Immucillin H Enhances NAD+ Boosting Effects of NR in Kidney
To determine how combining ImmH with NR raises NAD+ levels in different tissues and organs, Kropotov and colleagues injected mice with 400 mg/kg of NR with or without 2.5 mg/kg of ImmH. They then measured NAD+ levels from the blood, kidney, and liver. Co-treatment with ImmH and NR led to an increase in NAD+ in the kidney that surpassed treatment with NR only. These findings suggest that NR is more effective at increasing NAD+ in the kidney when combined with ImmH.
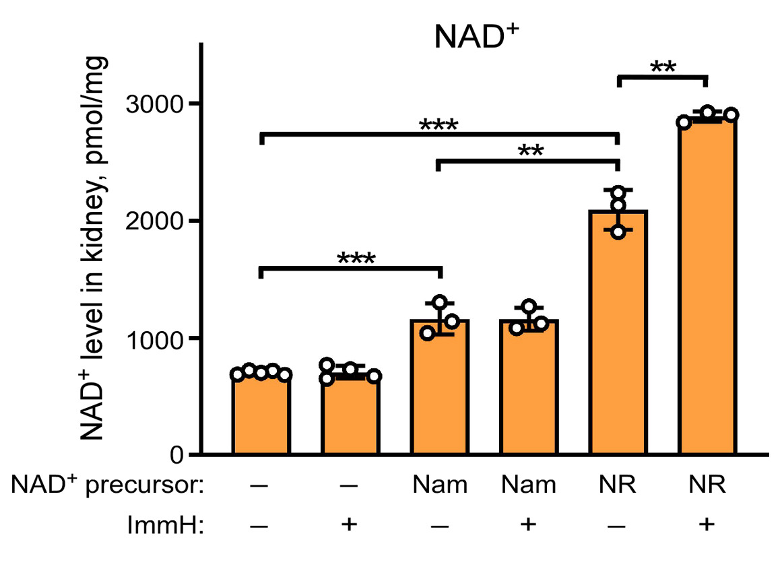
Overall, the findings of Kropotov and colleagues demonstrate that preventing the breakdown of NR with ImmH increases the synthesis of NAD+, at least in the kidneys. Since only blood, liver, and kidney NAD+ levels were measured, it is possible that ImmH also enhances the effect of NR in other tissues like skeletal muscle and the brain. However, additional studies will be needed to confirm this.
Is NR the Right Precursor for Replenishing NAD+?
While PNP inhibitors have been shown to treat age-related urinary tract dysfunction and are approved for the treatment of cancer, it is unclear whether they should be considered in combination with NR for the anti-aging benefits of NAD+ replenishment. While a study has shown that NR can improve insulin sensitivity and protect mice from weight gain, these results were not replicated in obese men. On the other hand, NR has been shown to increase skeletal muscle NAD+ levels and reduce inflammation in older adults, corroborating with rodent studies. It is unclear how putting ImmH in the mix would affect these results.
It may be that NR works better in some organs and tissues than others depending on the level of PNP found in each organ. In this case, a PNP inhibitor like ImmH would only be necessary for organs with high PNP levels. However, it may be easier to bypass NR and PNP altogether by supplementing with the more direct NAD+ precursor NMN. NMN has been shown to raise blood NAD+ levels in humans. Still, more studies are needed to determine the effect of NMN on age-related conditions like obesity and muscle inflammation.