Key Points:
- NAD+ therapy has gained widespread attention in the field of longevity, with endorsements from celebrities like Hailey Bieber, Jennifer Aniston, and Shannon Sharpe.
- NMN and NR are NAD+ precursors that help replenish NAD+ levels, and studies suggest they can enhance muscle strength, boost physical performance, reduce inflammation, and provide neuroprotection.
Despite the vast wealth and cutting-edge interventions available, even the most influential celebrities cannot avoid the inescapable reality of aging – succumbing, as we all do, to the steady progression of our body’s decline. In a determined bid to combat this inevitable process, many have turned to advanced longevity treatments, with nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) therapy emerging as a leading contender.
The recent surge in interest surrounding NAD+ and its precursors – nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) and nicotinamide riboside (NR) – is fueled by a confluence of scientific breakthroughs and endorsements from high-profile celebrities. Prominent figures such as Hailey Bieber, Kendall Jenner, and Jennifer Aniston have publicly shared their experiences with NAD+ therapies. “I’m going to NAD for the rest of my life, and I’m never going to age,” declared Hailey Bieber to Kendall Jenner in a 2022 episode of Keeping Up With The Kardashians. Onscreen, Bieber and Jenner were seen receiving intravenous NAD+ infusions, while Aniston praised her weekly NAD+ IV treatments as “the future” in an interview with The Wall Street Journal.
Even professional athletes are taking notice. NFL Hall of Famer Shannon Sharpe, known for his dedication to fitness and longevity, has also incorporated NAD+ precursors into his wellness regimen, further signaling the growing appeal of this advanced therapy.
The Scientific Basis of NAD+ and Its Role in Cellular Health
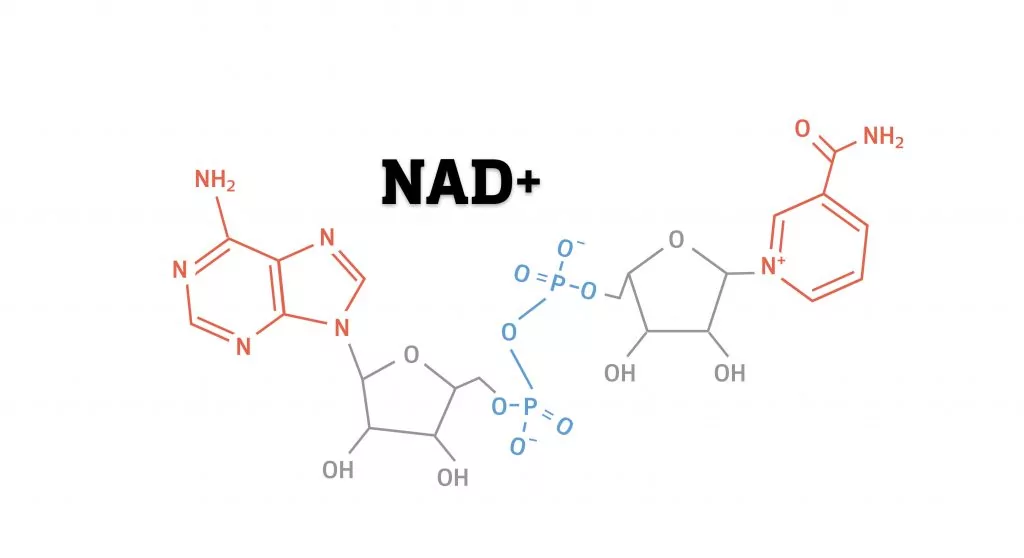
NAD+ is an essential coenzyme present in every cell of the human body, necessary for numerous biological processes, including energy metabolism, DNA repair, and mitochondrial function. It functions as a molecular “shuttle bus,” transferring electrons from one molecule to another to generate energy, primarily within the mitochondria – often referred to as the “powerhouse of the cell.” Without sufficient NAD+ levels, our cells would fail to generate the energy needed to maintain vital functions, leading to cell death and, ultimately, tissue degeneration.
The significance of NAD+ is not limited to energy production. It also fuels enzymes like sirtuins and PARPs (Poly ADP-ribose polymerases), which play key roles in maintaining cellular health. Sirtuins, often called “guardians of the genome,” regulate metabolism, promote DNA repair, and help preserve mitochondrial integrity, directly influencing cellular longevity.
However, NAD+ levels decline with age, a phenomenon observed across multiple tissues including muscle, liver, brain, and skin. This reduction is linked to diminished DNA repair and a decline in mitochondrial health, making the body more susceptible to age-related diseases such as neurodegeneration, cardiovascular disease, and metabolic disorders.
Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN): A Direct NAD+ Precursor
NMN, a direct precursor of NAD+, has gained considerable attention for its ability to replenish NAD+ levels effectively. Structurally, NMN is composed of a phosphate group, a ribose sugar, and a nicotinamide base, and it is only one enzymatic step away from being converted to NAD+. Some scientists posit that this proximity to NAD+ synthesis explains why NMN is considered one of the most efficient supplements for boosting NAD+ levels.
According to research, oral supplementation with NMN significantly increases NAD+ levels in multiple tissues. Recent studies have identified a specific transporter protein, Slc12a8, which facilitates the direct absorption of NMN into cells, making it readily available for conversion to NAD+. This efficient uptake distinguishes NMN from other NAD+ precursors, such as NR, which also boosts NAD+ but requires a slightly more elaborate conversion process.
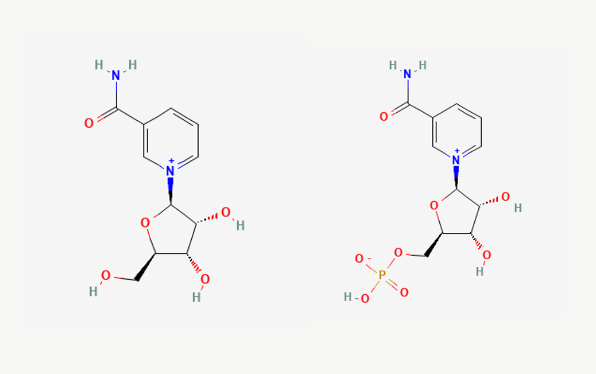
Nicotinamide Riboside (NR): An Alternative NAD+ Booster
NR is another NAD+ precursor that belongs to the vitamin B3 family. Structurally, NR is smaller compared to NMN due to the absence of a phosphate group, which can make it more easily absorbed by cells. After entering the cell, NR is converted to NMN, which then enters the NAD+ biosynthetic pathway, ultimately resulting in increased NAD+ levels.
The smaller size of NR has led some researchers to believe that it may be a more efficient precursor for increasing NAD+ levels, as it may bypass some of the potential absorption challenges faced by larger molecules like NMN. However, evidence of the Slc12a8 transporter suggests that NMN can also be absorbed directly into cells, which may make NMN just as efficient —, if not more so.
In studies, NR has been shown to effectively increase NAD+ levels in various tissues, although its efficacy has varied in different contexts. For instance, NR supplementation raised NAD+ levels in the blood and improved markers of inflammation – a hallmark of aging – particularly in older adults. However, NR did not significantly boost muscle NAD+ levels in older populations, suggesting its benefits may be tissue-specific. Furthermore, NR combined with other antioxidants has been shown to enhance these effects, particularly in slowing neurodegenerative diseases like ALS and improving cognitive outcomes in Alzheimer’s patients.
The Celebrity Appeal of NAD+ and What Human Studies Reveal About Its Efficacy
The use of NAD+ by celebrities has brought this once niche therapy into the mainstream, often showcasing it as a luxurious wellness treatment. Clinics like Modern Age in New York and resorts such as the Four Seasons in Maui offer NAD+ IV therapy for a premium price, targeting individuals seeking both anti-aging and wellness benefits. These high-profile endorsements have also sparked interest in accessible alternatives like oral NMN and NR supplements.
Human studies on NAD+ precursors are increasingly highlighting their potential to mitigate aging effects. Accordingly, these trials indicate that NMN supplementation improves several age-related parameters, such as physical performance, sleep quality, and insulin sensitivity. For instance, doses of 250 to 500 mg of NMN have been shown to increase muscle and white blood cell NAD+ levels, improve muscle oxygen utilization, and enhance exercise capacity in middle-aged adults.
Similarly, NR supplementation has been shown to raise blood NAD+ levels significantly. NR also appears to be particularly effective in reducing systemic inflammation. However, it should be noted that NR did not significantly improve muscle NAD+ levels in older populations, suggesting that NMN might be a more effective precursor in this regard, especially where muscle health and metabolic function are concerned.
Is NMN or NR Better?
Studies have consistently shown that boosting NAD+ levels with NMN or NR can counter age-related deficits across various tissues. NMN has shown particular promise in enhancing physical performance and improving insulin sensitivity, as evidenced by its effect on muscle strength, mobility, and metabolic health in older adults.
NR, on the other hand, has shown mixed results depending on the specific tissue and age group. While NR is effective at reducing inflammation and potentially mitigating the effects of neurodegeneration, its efficacy in improving physical performance appearsseems more limited compared to NMN. Furthermore, the effectiveness of NR tends to increase when combined with other compounds, such as pterostilbene and N-acetylcysteine, and enhances its anti-inflammatory effects.
Is NAD+ The Future of Aging Intervention Technologies?
The growing popularity of NAD+, NMN, and NR, driven by celebrity endorsements and ongoing scientific research, is attracting serious attention in the field of age-related disease prevention. Although further human trials are required to validate long-term benefits, current research demonstrates the potential of these supplements to improve cellular health, enhance metabolic function, and slow the progression of age-related decline. NAD+ may not yet be the definitive solution to halt or reverse aging, but its demonstrated ability to enhance energy metabolism, support DNA repair and improve cellular resilience warrants serious consideration as a promising aging intervention technology that can enhance healthspan and longevity.