Key Points:
- Treatment with CoQ10 attenuates age-related deficits in motor function in middle-aged mice, specifically coordination.
- Middle-aged mice treated with CoQ10 exhibit increased oxygen consumption, leading to improved mitochondrial function in the brain.
- CoQ10 treatment enhances the firing of neurons in the motor cortex – the brain region responsible for generating signals that precisely coordinate movement.
While the youth take advantage of their seemingly unbreakable bodies, adults are met with the inescapable reality of aging, with many succumbing to the inevitable decline of muscle function and fitness. Adults are burdened with these deficits, in part, due to impaired mitochondria – our cellular powerhouses – and brain dysfunction, which increases susceptibility to poor coordination and limited dexterity. Furthermore, these age-related abnormalities can be tied to the absence of vital molecules, one being the natural antioxidant coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10), that naturally decline with age. Since CoQ10 is known to support mitochondrial function, researchers have wondered whether replenishing CoQ10 could delay age-related ailments like motor dysfunction.
In a new study reported in the journal Scientific Reports, researchers from the Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Gerontology in Japan found that treating middle-aged mice with CoQ10 significantly improved motor coordination and enhanced the function of mitochondria in the brain. What’s more, they showed that CoQ10 treatment boosted neuron activity, highlighting a potential mechanism for CoQ10’s protective effects against motor dysfunction.
CoQ10 Boosts Motor Function
Although routine physical activity and consuming a well-balanced diet are healthy lifestyle habits that help preserve muscle integrity and fitness, age eventually catches up. As we surpass our youthful state, coordination and strength whittle away. Inoue and colleagues investigated these two parameters in middle-aged (15-16 months old) mice and examined the effects of CoQ10 supplementation, which was given via drinking water.
First, the investigators employed the pole test to look for changes in motor coordination. Here, mice were placed at the top of a pole and evaluated based on their ability to position their body and feet downward and quickly descend to the base. The results showed that CoQ10 treatment significantly improved the ability of middle-aged mice to orient their bodies at the top of the pole properly. Additionally, treated mice took less time to descend to the base than untreated middle-aged mice, demonstrating increased coordination.
The Tokyo researchers then examined CoQ10’s effects on muscle strength, which is usually tied to better coordination. The investigators conducted a wire-hanging test, where the increased latency to fall signified superior strength. The findings showed that CoQ10 treatment did not affect strength in both young and middle-aged mice, highlighting that its benefits are limited to coordination.

CoQ10 Enhances the Electrical Firing of the Motor Cortex
Given that the observed benefits of CoQ10 on coordination did not result from enhanced muscle strength, Inoue and colleagues explored other factors that play a role in regulating coordination and movement, namely the mitochondria and motor cortex – the hub for generating signals for movement and coordination. Mitochondrial dysfunction is a natural part of aging, and studies show that impaired mitochondria compromise the function of neurons, which are essential for transmitting signals for movement. Moreover, the sufficient activity of neurons is paramount to the motor cortex’s health. Thus, healthy mitochondria are essential for the proper functioning of the motor cortex.
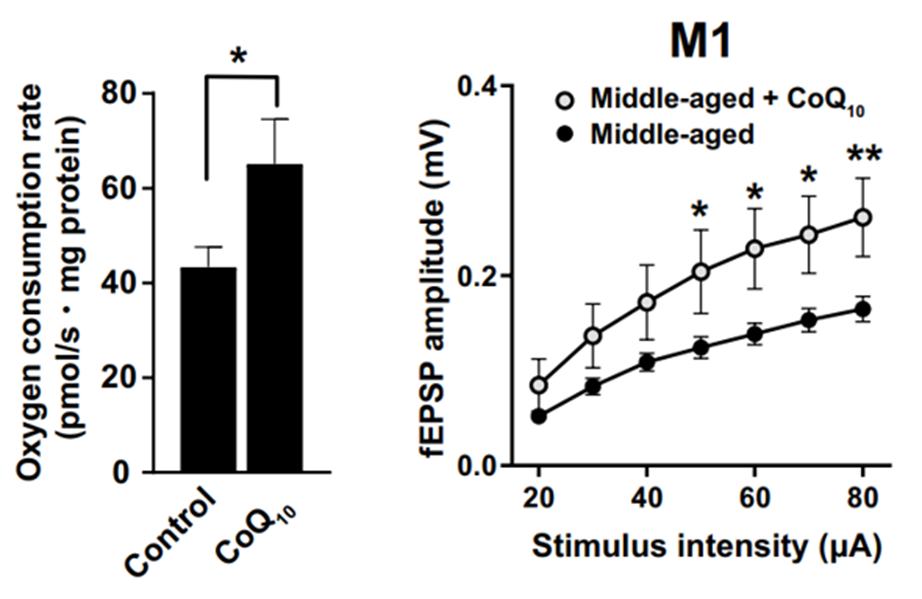
To examine mitochondrial function in the brain, the investigators quantified the oxygen consumption rate, a mitochondrial measurement that directly correlates to the production of ATP – the energy currency needed to power all cells, including neurons. The results showed that middle-aged mice treated with CoQ10 had a significantly higher consumption rate than untreated controls, showing improved mitochondrial function.
The investigators proceeded to calculate the field excitatory postsynaptic potential (fEPSP) amplitude of the motor cortex, a measurement that details the activity of neurons. Following CoQ10 supplementation, treated mice exhibited greater fEPSP amplitudes than untreated mice, demonstrating improved health and function of the motor cortex. Overall, the findings suggest that CoQ10 supplementation enhances motor function by boosting mitochondria and regulating the motor cortex.
Taking CoQ10
CoQ10 is a widely available dietary supplement, with research confirming its safety and low risk for minimal side effects like upper abdominal pain or nausea. The potent antioxidative properties of CoQ10 have led scientists to believe that taking CoQ10 could potentially mitigate oxidative stress-induced cognitive disorders like Alzheimer’s disease. Additionally, evidence suggests that CoQ10 attenuates symptoms of congestive heart failure. Notably, a recent study in 2022 also found that treating aged human skin cells with CoQ10 reduced senescent cells – growth-arrested cells that promote aging. Although it appears that CoQ10 holds some anti-aging properties, future studies are needed to fully understand its effects on humans. Remember, it’s always best to consult a healthcare professional before trying new supplements.