Key Points:
- NR treatment halts the progression of age-related hearing loss in mice.
- Treatment with NR boosts the communication between neurons that allow us to perceive sound.
Our senses allow us to formulate our perceptions of the world, with each sense adding a unique layer to the bigger picture. Unfortunately, our sense of hearing gets hit the hardest as we age, increasing the risk of age-related cognitive decline and dementia. Although treatments for age-related hearing loss (ARHL) are extremely limited, new research currently under review suggests that an NAD+ booster could potentially tackle this global health issue.
In a pre-printed (in the process of being peer-reviewed) article published in bioRxiv, researchers from the National Institute of Aging report that nicotinamide riboside (NR) exerts protective effects against hearing deficits in mice. Okur and colleagues show that supplementing mice with NR halts the progression of ARHL, particularly at high-frequency sounds. What’s more, they demonstrate that NR treatment improves the nerve impulses that allow us to hear.
NR Halts ARHL Progression
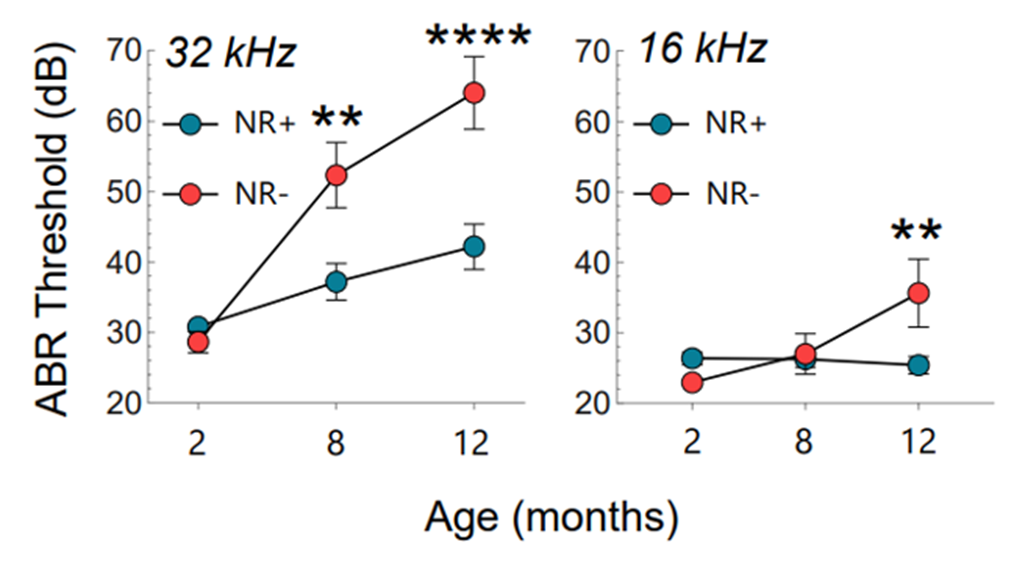
Research shows that nearly a third of individuals over the age of 65 succumb to ARHL, usually beginning with high-frequency sounds. Accordingly, Okur and colleagues evaluated the effects of long-term (10-month) NR supplementation in mice modeling ARHL at varying frequencies. At lower frequency sounds, there were no significant differences in hearing capacity between treated and untreated mice, with both groups requiring nearly equal volume to hear. However, NR-supplemented mice required significantly less volume than untreated mice to hear higher frequency sounds, demonstrating that NR halts the progression of ARHL, particularly at higher frequencies.
NR Improves Synaptic Transmission
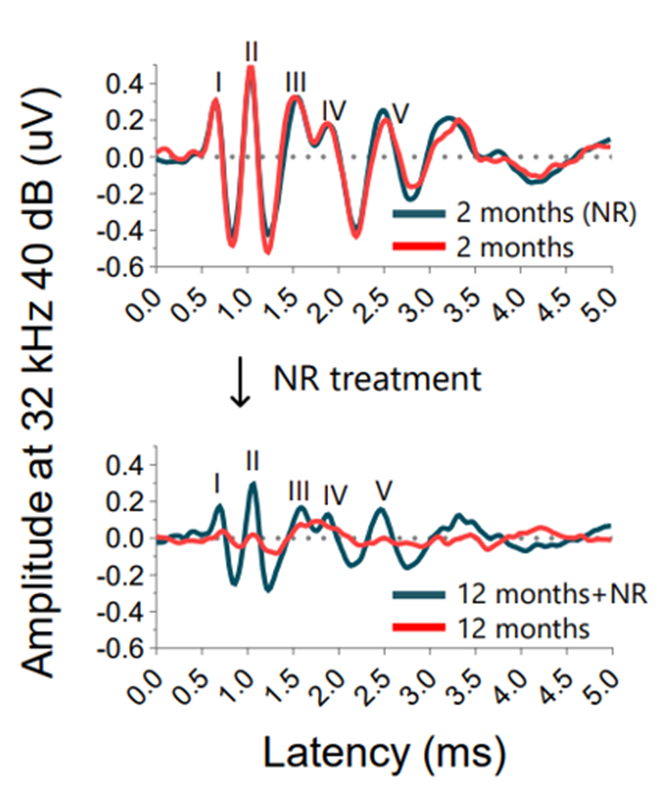
When we’re healthy, specialized neurons within our ear capture sound waves and convert them into electrical signals that traverse a series of brain regions along what is called the auditory pathway, ultimately allowing us to hear. Unfortunately, aging causes disruptions in the auditory pathway, leading to hearing loss. Okur and colleagues assessed the auditory pathway by measuring brain electrical signals in mice in response to sound, which when graphed form waves.
When young (2 months), all mice displayed nearly identical waveforms, indicating equal baseline hearing capacity. After aging for 10 months (equivalent to 50 years for humans), untreated mice produced graphs with flattened waves, which is indicative of a reduced auditory response. Notably, each wave on the graph highlights a specific region along the auditory pathway, the first wave corresponding to a region in the inner ear (cochlea). Okur and colleagues closely examined NR’s impact on wave 1 and found that supplementation sustained wave 1’s magnitude over the course of treatment, indicating preservation of the auditory pathway.
Are NAD+ Boosters the Future of Anti-Aging Therapeutics?
Research continues to unravel the full potential of NAD+ boosters as promising anti-aging therapeutics. Given that NAD+ is a life-sustaining compound that assists in DNA repair, boosts our cellular powerhouses (mitochondria), and regulates inflammation, finding ways to replenish NAD+ is of the utmost importance, considering that it declines with age. NAD+ boosters like NR have already been shown to exert neuroprotective effects against Parkinson’s disease. What’s more, studies in various animal models have shown that the NAD+ boosters nicotinamide and nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) delay age-related eye-degeneration, enhance cognition, and protect against cancer. Given that NAD+ boosters are widely available, it may be worth trying them to deter the negative effects of aging.