Key Points:
- Injecting old mice with MR409 increases their physical activity, hair growth, and survival rate.
- MR409 improves the systolic and diastolic function of the aging heart.
- The rejuvenation of mitochondria confers heart function improvements.
Growth hormone (a.k.a. human growth hormone) secretion declines with age and is associated with multiple aging effects, including diminished vitality and physical activity, muscle loss, and cardiovascular complications. However, scientists can now reduce these effects of aging in mice with peptides that stimulate growth hormone secretion.
Xiang and colleagues from Zhejiang University in China and Miami University in Florida report in the Journal of Cellular Physiology that MR409 increases the physical activity levels of old mice while increasing their probability of survival. MR409 also promotes fur growth. Additionally, MR409 improves heart function by rejuvenating the functional capacity of mitochondria.
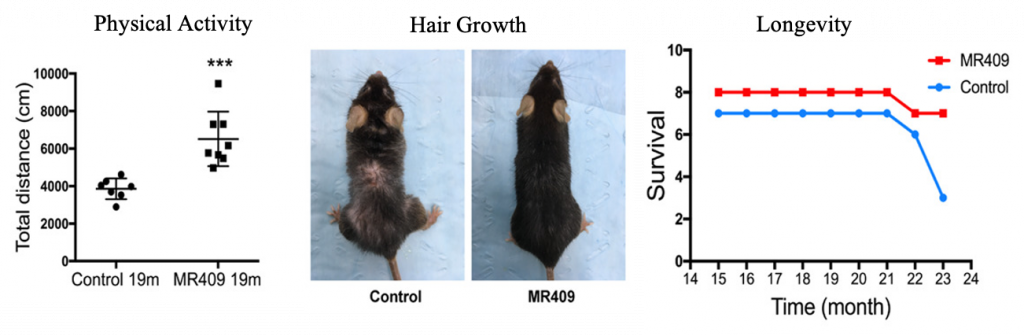
MR409 Reduces Multiple Effects of Chronological Aging
To study the impact of restoring growth hormone on aging, Xiang and colleagues injected 15-month-old mice with 10 µg/day of MR409 for four months. Old mice treated with MR409 traveled longer distances, suggesting improved mobility and vitality, and had more hair growth than their untreated counterparts. Furthermore, old mice treated with MR409 had a higher survival rate, demonstrating that MR409 may ameliorate multiple aspects of aging and increase lifespan.
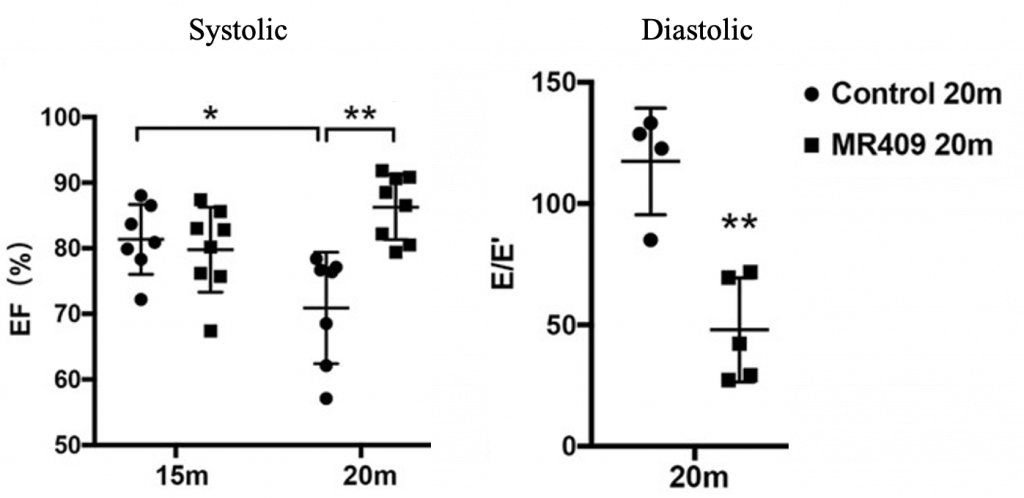
MR409 Improves Heart Function by Rejuvenating Mitochondria
Xiang and colleagues also measured the heart function of old mice treated with MR409, including the ejection fraction (EF), which reflects systolic (contraction) cardiac function, and the E/E’ ratio, which reflects diastolic (relaxation) function. MR409 improved both the EF and E/E’ ratio. As abnormal EF and E/E’ predict increased mortality risk, the findings suggest that MR409 could prolong lifespan by preventing or delaying cardiovascular complications.
The heart needs sufficient cellular energy to function, which mitochondria provide by consuming the oxygen we breathe. To investigate how MR409 improves heart function, Xiang and colleagues examined the oxygen consumption rate of mitochondria in the cardiac muscle cells of aged mice. The researchers found that the mitochondria from untreated aged mice consumed less oxygen, indicative of impairment. However, MR409 increased the mitochondrial oxygen consumption rate, demonstrating an improvement in mitochondrial health.
Schally’s MR409 May Reduce Other Effects of Aging
Dr. Andrew V. Schally, the 1977 Nobel Prize winner in medicine or physiology, and his lab developed MR409. MR409 induces many beneficial effects in animal models, some of which link to aging. MR409 reduces oxidative stress and inflammatory markers in a mouse model for colitis, promotes neural regeneration in a mouse model for stroke, and ameliorates kidney disease-induced heart failure in pigs. As research on MR409 progresses, we may see more studies examining its effect on aging.
How Do Growth Hormone Stimulators Affect Human Aging?
As we age, our muscles tend to atrophy and lose strength (sarcopenia) — putting us at risk for early death. Additionally, our body fat percentage tends to increase with age. Growth hormone stimulators — growth hormone secretagogues, like MR409, may contribute to reversing age-related changes in body composition.
For example, the orally active Capromoerlin increased the lean mass of older adults by about 3 pounds while improving physical activity. Other studies have shown that Sermerolin increases strength and skin thickness, decreases diastolic blood pressure, and increase lean mass by nearly 3 pounds in older adults. Notably, Tesamorelin increased GABA levels (the neurotransmitter that calms the brain) and improved cognition in some older adults.
Many growth hormone secretagogues are FDA-approved. Adverse events for these drugs include fatigue, insomnia, increased blood glucose, and insulin resistance. The long-term side effects are unclear. Furthermore, genetically removing the growth hormone receptor gene from mice has been shown to extend lifespan, so it is unclear how increasing growth hormone affects lifespan.