Key Points:
- Sesamol treatment prevents high-fat diet-induced obesity in middle-aged mice.
- Treatment with sesamol prevents obesity-induced metabolic syndrome.
- Sesamol activates longevity-associated proteins AMPK and SIRT1.
The sesame seeds on your Big Mac won’t help you lose weight, but according to a new study published in Food & Nutrition Research, sesamol — a compound present in sesame seeds and sesame oil — might. Hu and colleagues from Central South University in China report that sesamol helps prevent middle-aged mice from gaining weight while counteracting metabolic dysfunctions like high blood glucose, high cholesterol, muscle fat deposits, and oxidative stress. It seems to do so by activating AMPK and SIRT1, both associated with increased longevity. These findings suggest that sesamol could help with preventing age-related obesity.
Sesamol Prevents Weight Gain and Metabolic Dysfunction
To study obesity, Hu and colleagues induced obesity in middle-aged (about 40 years old in human years) mice by feeding them a high-fat diet. The obese mice were then fed 100 mg/kg of sesamol. Middle-aged obese mice treated with sesamol had less weight gain than obese mice not given sesamol and had body weights similar to young mice, suggesting that sesamol helps prevent age-related obesity in mice.
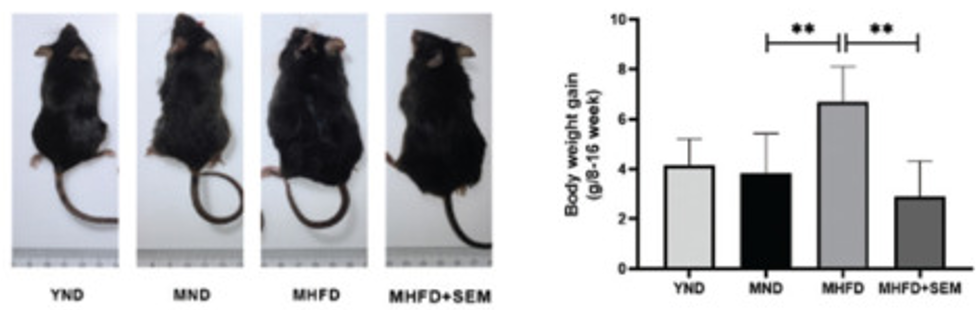
In addition to preventing weight gain, treatment with sesamol reduced insulin resistance and glucose intolerance, metabolic disorders that can lead to diabetes. Sesamol treatment also reduced blood levels of triglycerides (fats), total cholesterol, and LDL cholesterol (“bad”) and increased HDL cholesterol (“good”). These results demonstrate that sesamol helps to prevent obesity-induced dysfunction of sugar and fat metabolism in mice.
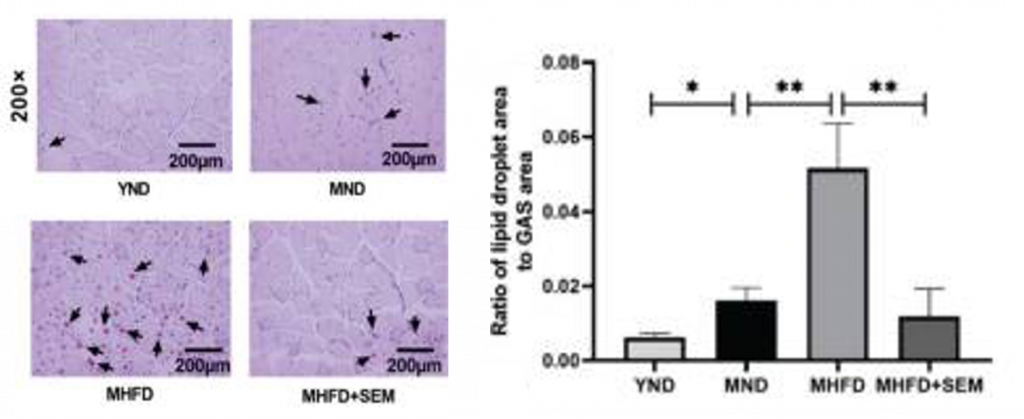
Markers of oxidative stress — a hallmark of aging that causes damage to cells — were reduced in both the blood and muscle of obese middle-aged mice treated with sesamol, suggesting that sesamol reduces the damaging effects of age-related oxidative stress. Obesity is characterized by increased body fat, which can cause fat accumulation in muscles. Sesamol treatment decreased the number of fat droplets in the muscle of obese middle-aged mice, another indicator of sesamol preventing obesity.
To determine how sesamol could prevent obesity, Hu and colleagues measured the muscle protein levels of AMPK and SIRT1, critical regulators of energy metabolism. AMPK and SIRT1 were reduced in obese middle-aged mice but restored by sesamol treatment. Since AMPK and SIRT1 maintain sugar and fat homeostasis in muscle, sesamol may enact obesity prevention by activating these proteins.
Supplementing with Sesame
Phytochemicals — chemicals produced by plants — like sesamol can possibly treat various diseases, including obesity and metabolic syndrome. For example, a compound in broccoli has effects similar to sesamol on obese mice. Polyphenols — a specific class of phytochemicals that activate SIRT1 — in particular, have even been used by celebrities to lose weight. While this study is one of the only of its kind to show that sesamol helps prevent obesity in mice, a meta-analysis has shown that sesame oil can reduce body mass index (BMI) in humans. Another meta-analysis showed that sesame consumption could reduce blood pressure in humans. A recent study showed that isolated sesamol could treat age-related cognitive deficits in mice by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation. Indeed, by reducing oxidative stress, sesamol is considered an anti-aging agent. Sesamol also has anti-cancer properties.
More research will be needed to parse out the benefits of sesamol versus sesame seed products, as sesame seeds contain other beneficial molecules, such as vitamin E. Additionally, sesamol is not readily sold as a dietary supplement. However, sesame extract is widely available, but it will be challenging to determine the concentration of sesamol in the extract unless indicated on the label. Otherwise, foods like tahini are made of sesame seeds, and sesame oil can be used for cooking, but consuming too much oil can be harmful. Thus, it is unclear how much of these foods would have to be consumed to achieve the benefits described in this study without receivng potential harms.