Key Points:
- Emergency hip surgery accelerates biological aging in elderly individuals.
- Pregnancy and COVID-19 infection also accelerate biological aging.
- The anti-inflammatory drug tocilizumab reduces COVID-19-induced accelerated biological aging.
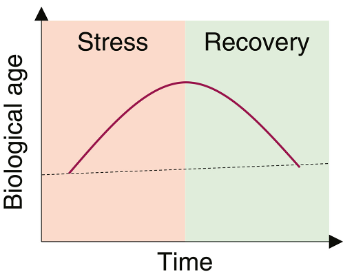
We all experience stress. Whether it be from work, relationships, financial concerns, or health issues, it’s a normal aspect of modern life. While chronic stress is known to contribute to accelerated aging and age-related disease, the effect of acute, highly stressful events on biological aging is not well understood.
Now, researchers from Harvard and Duke, the Karolinska Institute in Sweden, UCLA, and more report in Cell Metabolism that stressful events of varying duration promote temporary biological age acceleration. Specifically, Poganik and colleagues show that emergency hip surgery, pregnancy, and COVID-19 infection increase biological age, as determined by second generation aging clocks. They further show that biological age is reversed upon recovery from these stressful events.
“This finding of fluid, fluctuating, malleable age challenges the longstanding conception of a unidirectional upward trajectory of biological age over the life course,” say the authors.
Stress Accelerates Aging
Poganik and colleagues hypothesized that an acute, highly stressful event might accelerate biological aging. To calculate biological age, they isolated DNA from blood samples and measured DNA methylation (DNAm) — patterns of chemical groups attached to our DNA that alter gene activation. DNAm changes with age and varies between individuals. Thus, biological age can be higher or lower than chronological age. Notably, if biological age is higher than chronological age, then biological age is considered accelerated.
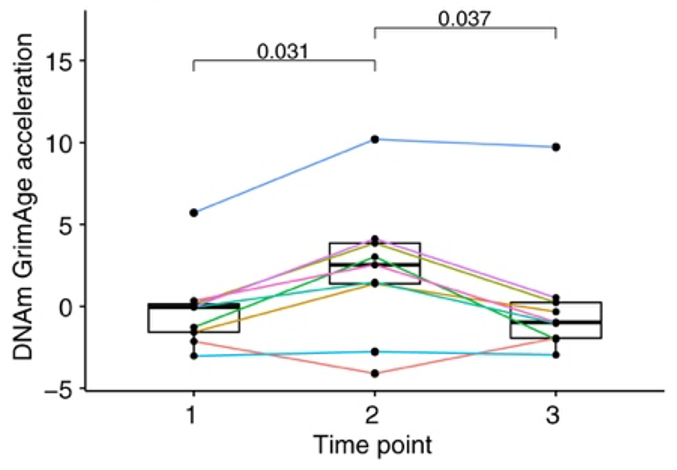
To determine if emergency surgery accelerates biological age, the researchers used blood samples from previous studies. These blood samples were taken from surgery patients immediately before, the morning after, and a few days after surgery. Biological age was calculated at each of these time points. The results showed that patients who underwent emergency hip surgery had an acceleration in biological age the morning after surgery, which was reversed a few days after surgery.
“The patients in this cohort were elderly (mean age 77.9 years), implying, surprisingly, that even people of advanced chronological age have the capacity to reverse a stress-induced increase in their biological age,” noted the authors.
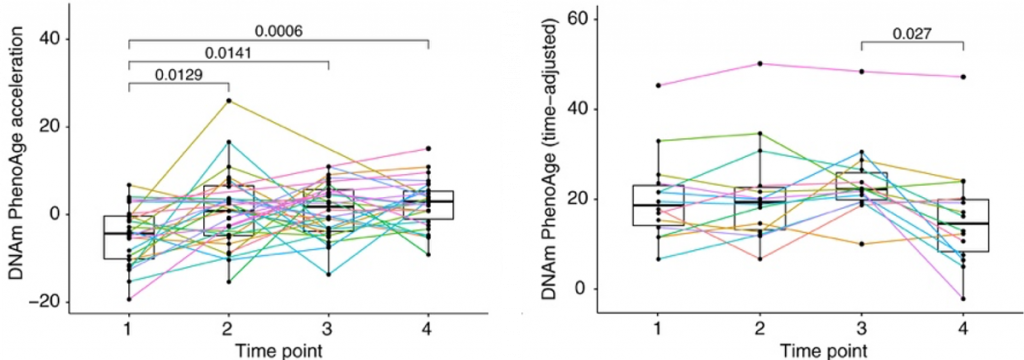
Poganik and colleagues next examined pregnancy, a physiologically stressful event that puts a high demand on the organs to support fetal development. To do this, the researchers analyzed blood samples from previous studies of pregnant women. From a cohort of Swedish women, they found that biological age accelerated over the duration of the pregnancy. However, these women were only tracked until a few days after delivery and had not yet recovered.
In another dataset, American women were tracked throughout their pregnancy up until six weeks postmortem, giving them time to recover. For this dataset, chronological age had to be estimated. The results showed that their biological age was reduced six weeks after delivery compared to during pregnancy, indicating a reversal in biological age. Combined with the results from the Swedish study, these findings suggest that biological age progressively accelerates during pregnancy and then reverses after the baby has been delivered.
Poganik also analyzed blood samples from a dataset of COVID-19 patients who were admitted to an intensive care unit (ICU) and survived the infection. Since the patients were already admitted to the ICU at the time of the first blood draw, their biological age was assumed to already be accelerated. It was found that seven days after being discharged from the ICU, the biological age of women but not men was reduced. These findings suggest that biological age acceleration was reversed only in women recovering from COVID-19.
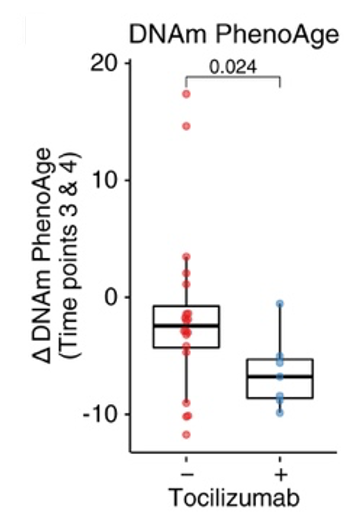
The researchers next investigated the effect of COVID-19 interventions, which were experimental at the time (dataset from March-June 2020). The results showed that as opposed to the anti-malarial drug hydroxychloroquine and the antiviral drug remdesivir, the anti-inflammatory drug tocilizumab lowered the biological age of COVID-19 patients compared to COVID-19 patients who did not receive this intervention. These findings suggest that tocilizumab could prevent biological age acceleration induced by COVID-19.
Overall, the findings highlighted here suggest that biological age is accelerated by highly stressful life events. The authors add:
“The findings also imply that severe stress increases mortality, at least in part, by increasing biological age. This notion immediately suggests that mortality may be decreased by reducing biological age and that the ability to recover from stress may be an important determinant of successful aging and longevity.”
Ways of Reducing Biological Age
Not all types of biological stress accelerate biological aging. In fact, it seems that certain types of acute physiological stress can decelerate biological aging. For example, a special biological age-lowering diet combined with several supplements, exercise, and sleep has been shown to reduce biological age in women. This and other studies suggest that exercise, a physiologically demanding activity, reduces biological age.
The 45-year-old tech millionaire Bryan Johnson follows a strict protocol to reduce his biological age. Johnson practices caloric restriction, where he eats fewer calories and doesn’t eat for most of the day. This is physiologically (and can be psychologically) stressful. His measurements and other studies suggest that caloric restriction and fasting reduce biological age. Additionally, the results of Poganik and colleagues suggest that tocilizumab can reduce biological age, but it is unknown whether this is true in non-COVID-19 patients.