Key Points
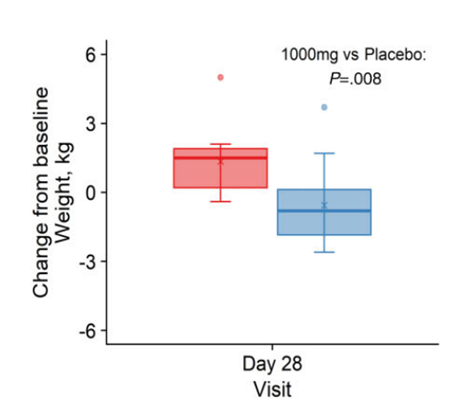
- Two 1,000 mg doses of nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) daily for 28 days significantly reduces body weight in overweight or obese middle-aged and older adults.
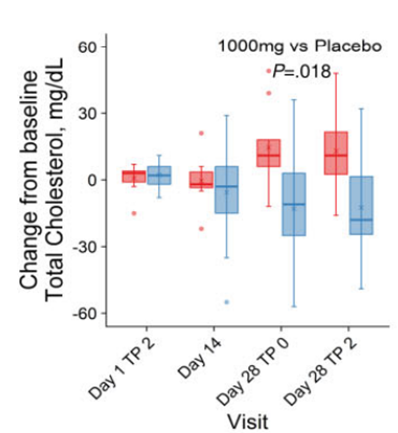
- This NMN dosing regimen significantly reduces total blood cholesterol, including low density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol that causes arterial cholesterol buildup.
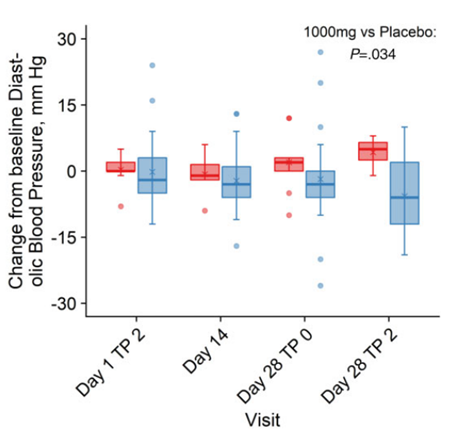
- NMN significantly curtails diastolic blood pressure, a key contributor to high blood pressure.
Research has shown that cellular levels of the essential molecule for cell energy generation, mitochondrial production, and DNA repair – nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) – drop as we age. Scientists have postulated that this age-related declining cellular NAD+ contributes to age-associated diseases. Rodent studies have shown that NAD+ augmentation improves healthspan by enhancing cardiovascular function and metabolism. Human studies have shown NMN substantially increases blood NAD+ levels in overweight or obese adults, however, whether this confers physiological benefits has yielded mixed results.
Published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, Bhasin and colleagues from Harvard Medical School show that supplementing with the MIB-626 NMN formulation significantly cut body weight in overweight or obese adults. Testing the study participants’ blood revealed that the NMN treatments reduced total cholesterol, including a harmful form of cholesterol – LDL. Heart function measurements also showed that NMN significantly reduced blood pressure when blood fills the heart – diastolic blood pressure – which contributes to high blood pressure (hypertension) when elevated. These findings suggest NMN confers physiological benefits like reduced body weight, which should be examined in future clinical trials with more participants and a longer duration.
NMN Reduces Body Weight, Cholesterol, and Blood Pressure
Bhasin and colleagues administered two 1,000 mg doses of NMN daily for 28 days in middle aged and older overweight or obese adults to find out how it affects key physiological parameters. They found that NMN significantly cut body weight compared to participants who didn’t take NMN following the 28-day treatment regimen. These findings suggest that NMN confers metabolic benefits as shown with a substantial indicator of metabolic health – total body weight.
To measure NMN’s effects on cardiovascular health, Bhasin and colleagues turned to blood cholesterol readings. They found NMN significantly reduced total cholesterol levels, along with harmful LDL cholesterol that accumulates in vasculature leading to heart problems. These findings support that NMN can help the cardiovascular system by reducing cholesterol levels.
To find out whether NMN improves heart function, Bhasin and colleagues measured diastolic (blood filling the heart) and systolic (when the heart pumps blood) blood pressure. Interestingly, NMN curtailed diastolic blood pressure, a key contributor to high blood pressure (hypertension) when high, but not systolic blood pressure. These results suggest that taking NMN may be a way to alleviate hypertension in overweight and obese adults.
NMN’s Benefits Could Be Extended with a Longer Dosing Regimen
The study provides the first evidence that NMN reduces body weight in middle aged and aged overweight and obese adults. The short study duration draws into question what anti-obesity benefits might come from supplementing with 2,000 mg of NMN per day for more extended periods. One would think that a longer study duration may enhance NMN’s anti-obesity benefits. Moreover, NMN could facilitate larger cholesterol and blood pressure reductions with longer study durations.
Another key limitation of the study was that it only had 21 participants taking NMN. The study didn’t show any effects from taking NMN on muscle strength or recovery time, but with more participants and a longer duration, a muscle performance effect from NMN is possible. As such, a future study could include a workout regimen while taking NMN to find whether NMN improves strength and endurance with a workout routine.
In essence, results from this study bode well for overweight and obese adults trying to lose weight who’d like to try NMN. A factor to consider is that the dosages used in this study were 2,000 mg per day, which are higher than most other studies. Using doses this high may be pricey, costing well over $150 per month.