Key Points:
- NR restores exercise capacity as measured with time run before exhaustion in mice with radiation-induced premature aging.
- NR reverses lowered white and red blood cells from radiation.
- NR alleviates radiation-triggered cell senescence — an aging-associated state where cells stop proliferating and release inflammatory molecules — in stem cells.
Radiotherapy involving the treatment of cancer patients with ionizing radiation against tumors comes with a troublesome risk — it contributes to accelerated aging. A faster pace of aging leads to chronic health conditions in 73.4% of childhood cancer survivors. Surprisingly, no countermeasures against radiation-induced premature aging have been developed.
Published in Aging Cell, Li and colleagues from the Chinese Academy of Medical Science & Peking Union Medical College show that NR restores physical health, as shown with improved exercise capacity, in radiation-exposed mice. The researchers also show that NR revamps the numbers of white and red blood cells following radiation exposure. Furthermore, NR alleviates senescence in bone marrow-derived blood cell precursor stem cells. Since the body’s blood production system (hematopoietic system) receives an abundance of damage during radiation, these findings suggest that NR reverses radiation’s injurious hematopoietic effects to restore physical capacity.
NR Improves Physical Functioning, Increases Blood Cell Counts, and Reduces Blood Stem Cell Senescence
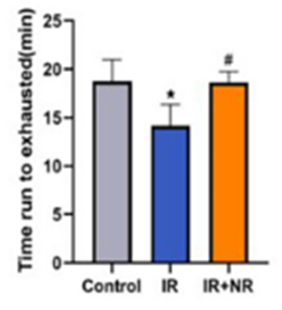
Since radiotherapy drives accelerated aging and chronic diseases, Li and colleagues tested its effects on physical fitness. The China-based researchers found that radiation significantly reduced physical fitness as measured with lower times run before exhaustion. Interestingly, NR supplementation restoratively increased times run to exhaustion in radiation-exposed mice. These results suggest that NR reverses radiotherapy’s detrimental effects on physical functioning capacity.
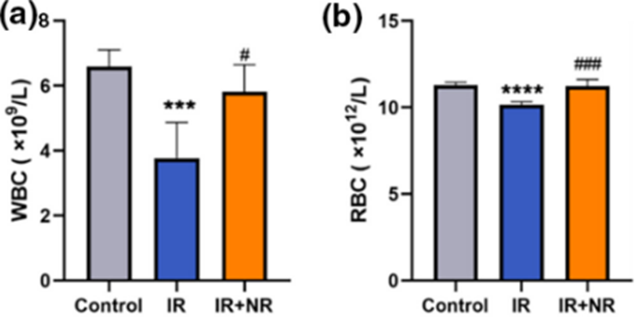
Since blood carries oxygen to influence exercise capacity and the hematopoietic system undergoes extensive senescence during radiotherapy, Li and colleagues measured how radiation affects blood cell numbers. They measured the numbers of white blood cells and red blood cells in circulation. While radiotherapy reduced white and red blood cell numbers, NR restored them. Since white blood cells counteract infections as part of the immune system and red blood cells carry oxygen to tissues throughout the body, these findings support that NR restores health against radiotherapy with increased blood cell numbers.
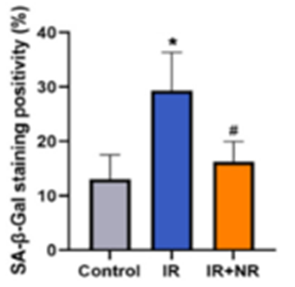
Because radiotherapy induces premature aging and since NR restores blood cell counts, Li and colleagues sought to find whether NR alleviates senescence in key, bone marrow-derived stem cells for blood cell production — Lin−Scal+c-Kit+ cells (LSKs). Intriguingly, they found that the radiotherapy exposure more than doubled senescent LSKs, which would inhibit their blood cell-producing capabilities. Supplementing radiation-exposed mice with NR, on the other hand, alleviated the LSK senescence.
These findings provide a connection between lowered senescence in LSKs, which would improve their capacity to produce blood cells, and increased blood cell numbers. As such, one way NR restores health against premature aging in radiation-exposed mice is by revamping the hematopoietic system against radiation-induced injury.
“Our results demonstrated that NR ameliorated the aging phenotypes in our mouse model. Furthermore, NR treatment alleviated LSKs senescence…” say Li and colleagues.
Other NAD+ Precursors Like NMN Likely Reverse Premature Aging from Radiotherapy
The study provides evidence that supplementing with a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) precursor like NR restores physical health against radiotherapy by restoring the hematopoietic system. NR likely restores blood cell-producing LSK cells with its antioxidant capabilities, which reduces inflammation. Since inflammation is a key contributor to aging, NR’s anti-inflammatory properties could serve as a principal way by which it reverses premature aging in radiation-exposed mice.
Other studies have shown that another NAD+ precursor, NMN, protects the intestinal wall against radiation-induced damage. In that study, researchers showed that NMN served as an antioxidant to confer its protective effects against radiotherapy. A main difference between Li and colleagues’ study and the NMN study was that Li and colleagues showed restored physical functioning capacity. Nonetheless, since NMN is also an NAD+ precursor, it’s likely that NMN also works to revamp the hematopoietic system against radiotherapy and restore exercise capacity.