Highlights:
- Urolithin A (UA), an important microbiome-generated metabolite, is only produced in 12% of the study’s participants.
- Due to differences in microbe abundances, subjects failed to convert dietary precursors into UA.
- Direct UA supplementation produces significantly higher levels of circulating UA indicators, as opposed to other UA sources like pomegranate juice.
Even if you follow the food pyramid’s guidelines, eating optimal portions of each food group, you still may not get all the necessary nutrients. That happens, in part, because if we don’t have the right mix of microbes in our guts — the microbiome — then we can’t convert food into the nutrients needed to power our cells. For example, many people don’t produce enough urolithin A (UA), a longevity-linked compound that promotes the healthy functioning of muscle and the cell’s power generators, the mitochondria. So, can we supplement with UA to bypass microbiome deficiencies?
In the European Journal of Clinical Nutrition, new research from Singh and colleagues detailed the first study on using direct dietary UA supplementation to overcome differences in microbiome composition in healthy individuals. The supplement used in the study containing UA recently was in the spotlight because Elon Musk’s mother Maye Musk — a registered dietician with multiple Master’s degrees — recently signed on as a spokesperson for the company to promote the product. Although the supplement had previously been shown to be safe, this study demonstrates the potential to improve mitochondrial health through supplements via the microbiome.
Why Do We Care About Urolithin A?
UA has been in the spotlight of aging science for quite some time. Previous studies have demonstrated UA’s ability to delay the onset of muscular aging in mice and replenish the levels of a vital energy-producing compound called nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+). Boosting NAD+ in mice has been shown to promote DNA repair, improve cardiac functions, and protect against age-associated metabolic disorders. Scientists are still figuring out if these beneficial effects can be translated to humans, but UA research may be a stepping stone that gets us closer to overcoming this barrier.
Pomegranate Juice Is Insufficient In Producing UA Subjects
Singh and colleagues categorized healthy subjects (aged 20-80 years) into three groups based on their circulating levels of UA glucuronide, the most common form of UA in the body, at baseline before any supplementation: No-Producer Group (no detectable UA-Glucuronide), Low-Producer Group (5-100 ng/mL UA-Glucuronide), and High-Producer Group (>100ng/mL UA-Glucuronide). Initial plasma analysis showed that 12% of healthy individuals exhibited detectable levels of circulating UA-glucuronide at baseline. What’s more, only 2% of those individuals were classified as high-producers. However, one day of pomegranate juice supplementation resulted in 40% of individuals displaying high-producer status. As most individuals failed to demonstrate gut-mediated production of UA, these results suggest that their gut microbiome lacks the necessary tools to transform dietary precursors into UA.
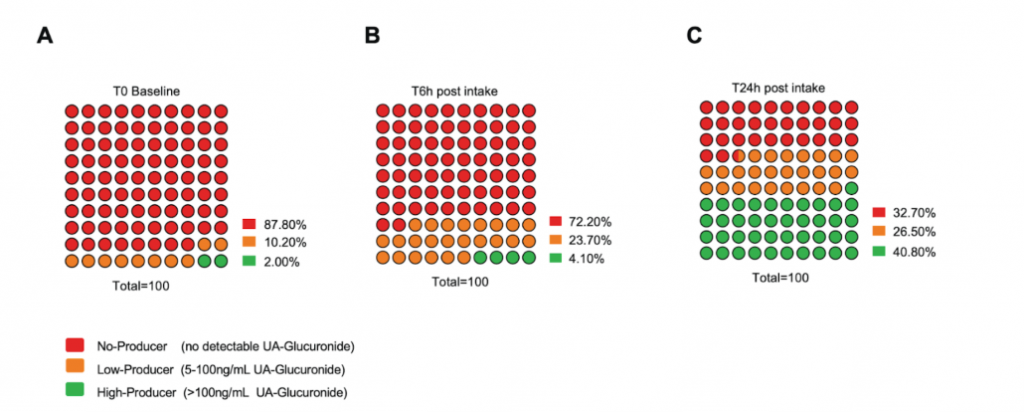
Gut Microbiome Composition Dictates UA-Producer Status
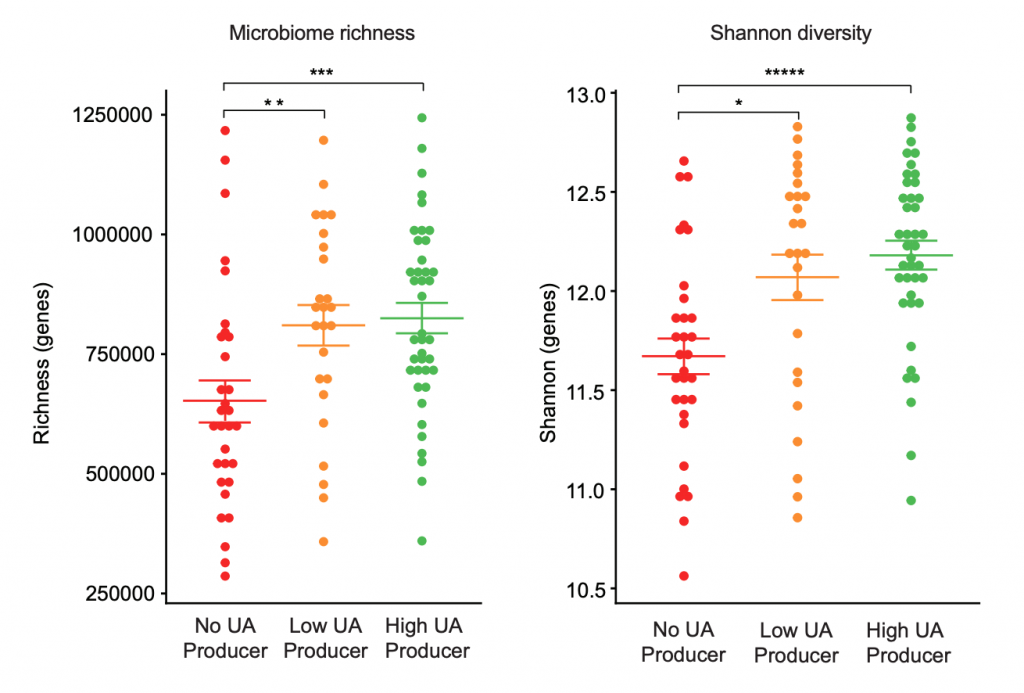
Singh and colleagues then collected fecal samples to characterize the microbiome composition among UA producers and non-producers. Analyzing each individual’s microbial genomes identified the relative abundance of species or genes (richness) within the microbial community. The results show that low-producers and high-producers of UA exhibited much greater microbiome richness and diversity over non-producers. These findings suggest that people require diverse and rich microbiomes to synthesize UA effectively.
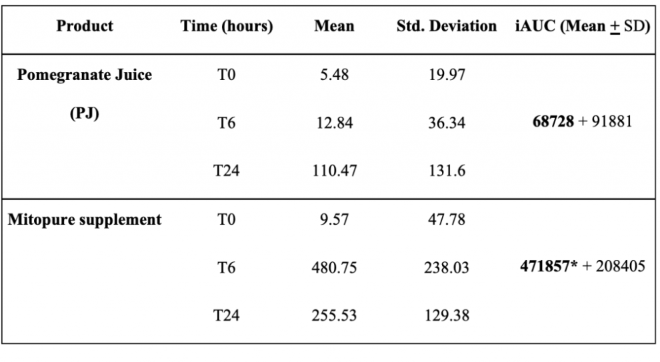
Direct UA Supplementation Produces Greater Circulating Levels of UA than Pomegranate Juice Supplementation
Given that most subjects failed to display significant circulating UA levels 24 hours post pomegranate juice supplementation, the research team examined whether direct UA supplementation could overcome the associated microbiome deficiencies. Subjects were given a powder supplement called Mitopure, containing 500 mg UA, and measurements of circulating UA glucuronide were taken at six and 24 hours after oral consumption. Plasma analysis revealed that Mitopure supplementation produced significantly higher circulating UA glucuronide concentrations than pomegranate juice supplementation. With most subjects displaying high-producer status, it is evident that direct UA supplementation overcame the subjects’ microbiome deficiencies. Moreover, these findings validate using direct UA supplementation instead of UA dietary precursors to promote UA synthesis.
Can UA Be Used as An Anti-Aging Supplement?
Given the findings of this study, it may be possible for humans to acquire the age-related mitochondrial benefits of UA with direct supplementation. Mitochondria are the vital internal batteries of our body. When these batteries malfunction, we’re susceptible to developing age-associated conditions ranging from heart disease to neurodegenerative disorders. One critical survival mechanism related to defective mitochondria is autophagy, where the cell disposes of protein waste, and recent studies suggest that UA can activate this essential metabolic process.
Interestingly, the mother of Elon Musk currently endorses Mitopure as the next big anti-aging supplement. “I’m hoping to live longer than my mom, and she lived to be 98. If this is going to continue to repair my mitochondria, I’m hoping that this will be the new anti-aging supplement to take,” said Elon Musk’s mother in a press release.
But even if you’re the mother of one of the wealthiest men in the world, touting a supplement isn’t going to push it through any regulatory hurdles. Whether UA on its own or in a product like Mitopure is effective in protecting human health or treating a condition, these supplements will have to be evaluated just like any other therapeutic compound, which is through clinical studies. So, testing is needed to see if UA has super charging capabilities in human mitochondria and any other beneficial effect on the body.